Texture Coordinates
Texture coordinates, also called UVs, are pairs of numbers stored in the vertices of a mesh.
These numbers are often used to stretch a 2D texture onto a 3D mesh, but they can be used for other things like coloring the mesh (see Vertex color), controlling the flow across the surface (see Flow map), etc.
Game engines commonly use two texture coordinates, U and V, for mapping the width and height of a texture. A third axis W can also be used for depth if you are using a 3D volume texture, but usually this coordinate is removed for efficiency.
Texture coordinates are measured in a scale of 0.0 to 1.0, with 0.0 and 1.0 at opposite sides of the texture. When a model has a UV distance greater than 1 (for example, UV goes from -1 to 2) then the texture will tile across the model.
These numbers are usually hidden from the artist, replaced by helpful visual representations of how the textures are projected. Planes, cylinders and spheres help the artist align the textures in a visual way, but it helps to know that games only see the UV numbers that these shapes create.
Contents
UV Best Practices
UVs for game art are not just about cramming things into a single sheet; they are also and just as importantly about:
- Making the UVs human-readable so that another artist can take care of the texturing. Meaning, orienting the islands the right way up and grouping parts in a way that makes them as instantly identifiable as possible.
- Furthermore, orienting the various panels vertically and horizontally allows for maximum clarity of decals and graphics since they would then naturally follow the orientation of pixels.
- Taking into account the fact that the asset needs to behave well when down-sampled. Therefore having the appropriate amount of padding around the islands.
Here are some examples extracted from MGS4 (Raiden, Raven, Wolf), Overwatch (Tracer, WidowMaker, Vampire Reaper), Valorant, Zenless Zone Zero, Deadlock, and Arms. These span over 3 generations of hardware, showing that things really haven't changed at all over the last 10+ years or so besides the generational increases in texture resolution.

Image by Pior "pior" Oberson from the Polycount thread UV layout.
While automatic packing can have its uses, it definitely takes a backseat in favor of the above factors in practice.
If two applicants had superficially similar portfolios but one used automatic packing on everything while the other showed care for manual UVs, the preference would go for the one demonstrating manual UVs as it tends to mean that the artist has more production experience under their belt.
UV Tutorials & Threads
For better LODs, straighten the perimeter edges of the UV shells. Dents or protrusions along an optimized edge are more likely to create visible seams. The edges don't have to be 90°, diagonal is fine, but the longer and straighter the edges, the better the model can avoid artifacts during reduction.
| UV mapping thought process. Images by Jesse "skankerzero" Sosa. | |||
- Head Unwrapping-Methods Polycount Forum thread.
- What is your prefeered UV unwrapping application? Polycount Forum thread.
- Do we really need to be Uv mapping in 2015? Polycount Forum thread.
- Seamless UVs for baking procedural textures in 3ds Max by Howard Day.
- UV Unwrapping Best Practice Factors & Priorities Polycount Forum thread.
- 3DS Max - UVing complex objects Polycount Forum thread, UVs for complex cylindrical-shaped meshes.
- Best techniques for packing UV’s Polycount Forum thread.
- An Introduction To UVMapping In 3d Studio Max by Ben Tate.
- UV Theory Polycount forum thread, how to plan good UVs.
- As it turns out, we all suck at unwrapping? Polycount forum thread.
- Step-by-Step Techniques for Tiling Textures in 3ds Max - by Chris Holden, how to make Texture atlases.
- Organic rock UV seams Polycount forum thread, how to create good UVs for spheroids.
- Unwrapping a sphere Polycount forum thread, good methods for UVing spheres. For sphere modeling tips see SphereTopology.
- First-Person Weapon UVs by Joe 'EarthQuake' Wilson, good weapon UVs.
- Maya / Mudbox: Street Cop Workflow by Mashru Mishu, good character UVs.
- What's an 8-sided tiled texture ? Polycount forum thread, how to edit textures so you can rotate and mirror them on adjacent polygons without seams.
- Light map#Light_Map_Texture_Coordinates
- Texture atlas
UV Address Modes
Image by Open.GL.
There are four common methods for controlling how a texture is rendered when the UVs go beyond the 0-1 square. These methods can be chosen with a Shader.
- Repeat or Wrap is usually the default. The texture will tile.
- Mirror causes the texture to be flipped along each edge. Mirror has a tendency to create Rorschach/butterfly artifacts, but can be useful in certain situations like fences or railings.
- Clamp causes the edge pixels to stretch outwards beyond the edges of the texture. Clamp is great for use with Cubemaps, since when the texture is filtered you don't want seams to appear along the edges of each cube face.
- Border causes a solid color to appear outside the edge of the texture. Border is good for use with Decals, since you don't want the edges to tile and cause rendering seams.
UDIM is another address method, not used in games. UDIM allows multiple textures to be used by a single model, by offsetting the textures in whole units across UV space. UDIM is useful for texturing in television and film to increase the number of textures per model in a logical and uniform way.
Usually a single texture pattern is tiled by UV'ing the model outside the 0-1 square. However, multiple tiling textures can be arranged in a Texture atlas as sub-tiles and cropped out using a shader. The shader for this is more expensive than traditional texture tiling, but can be used if you are limited by the number of textures you can use.
UV Tools
Standalone
A standalone tool is one which is not directly integrated into another 3D package.
- UV Packer IPackThat Polycount Forum thread
- IPackThat MODO script Polycount Forum thread
RoadKill by Francis O'Brien
UVLayout by Headus
3ds Max
- TexTools
- PolyUnwrapper
- Texture Atlas Generator
- turboTools
- Normalize UVs Maxscipt
- LCSM Unwrap
- 3ds Max Bridge to Headus UV Layout
- 3ds Max Bridge to Roadkill
- morphMap
Maya
- Castor Lee's Auto UV Mapper
- Maya Bridge to Headus UV Layout
- Nightshade UV Editor
- Texturing Scripts on CreativeCrash.com
- UVDeluxe
Softimage / XSI
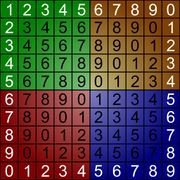
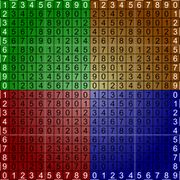
UV Map Grids
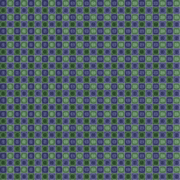
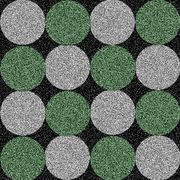
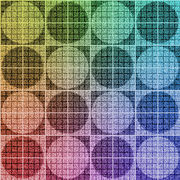
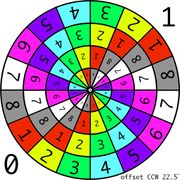
The grid is a texture to use while unwrapping a mesh. Sometimes called a custom UV map template, a UV checker, or a test grid.
Good things to have in a UV map grid:
- A large checker grid to see large distortions.
- A fine per-pixel grid to see small distortions.
- Circles help with solving distortion, as it's easier for the human eye to see when a circle is distorted than a square.
- Unique colors across the map, to see where the UV is tiling.
- Letters and/or numbers to see when the UV is reversed.
- Letters and/or numbers to see where a mesh feature is located in UV space.